Here in Part 4 of the Ten Most Unusual Motorcycles, we look at a Suzuki which has gone on to a cult status.: The GSX1100 and GSX750 Katana.
Please click here for Part 1 (Suzuki RE5), here for Part 2 (Honda CBX1000), and here for Part 3 (Yamaha GTS1000).
The name “Katana” alludes to the Japanese Samurai sword, hence the symbol. The name and logo went on to grace many other Suzukis thereafter. Here in Malaysia, remember Suzuki Best and RG owners would apply the stickers to their bikes? That was part of the Katana’s legacy.
The Suzuki Katana was designed by Hans Muth and his company, Target Design. Muth was the ex-design chief at BMW and was tasked with overhauling the Japanese manufacturer’s image.
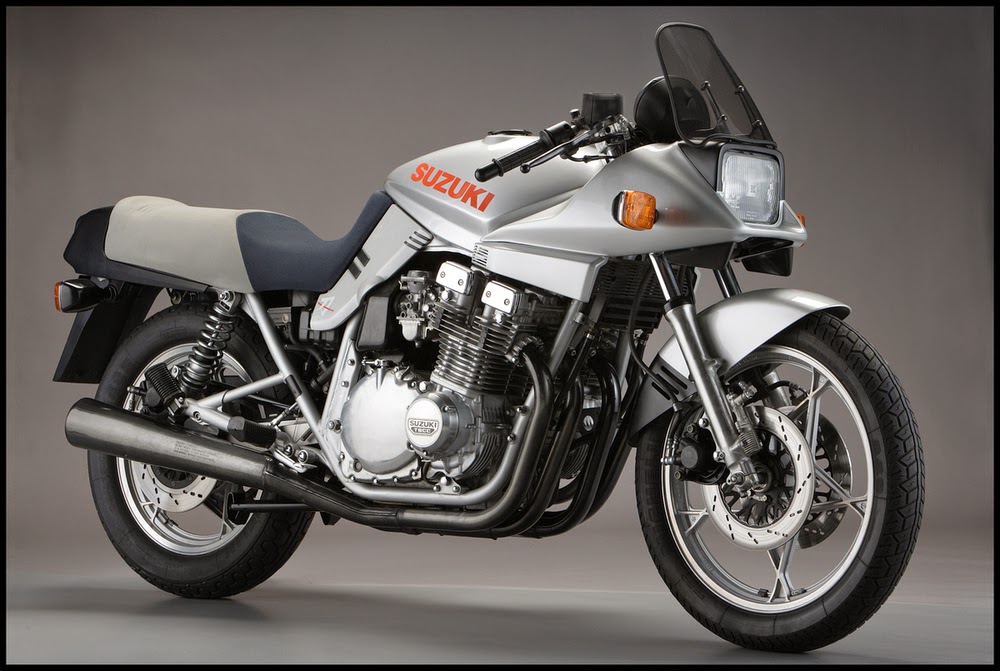
Suzuki chose one of Muth’s designs and the first production Suzuki GSX1100S Katana was made public in 1980. While they didn’t follow the concept’s design to the letter, many important design cues were adopted.
The design was avant-garde from the cookie cutter bikes of the era. Most notable feature was how the rear part of the fuel tank and front portion of the seat blended together. Also, the passenger’s seat was slightly raised and coloured differently, lending to a solo-seater look. Yes, it was the Suzuki Katana that started it.
The 1075cc, air-cooled, DOHC, inline-Four produced 109.5 bhp and Suzuki claimed the Katana as being the fastest production motorcycle. It ran the ¼-mile (400m) in 11.9 seconds at 191.5 km/h.
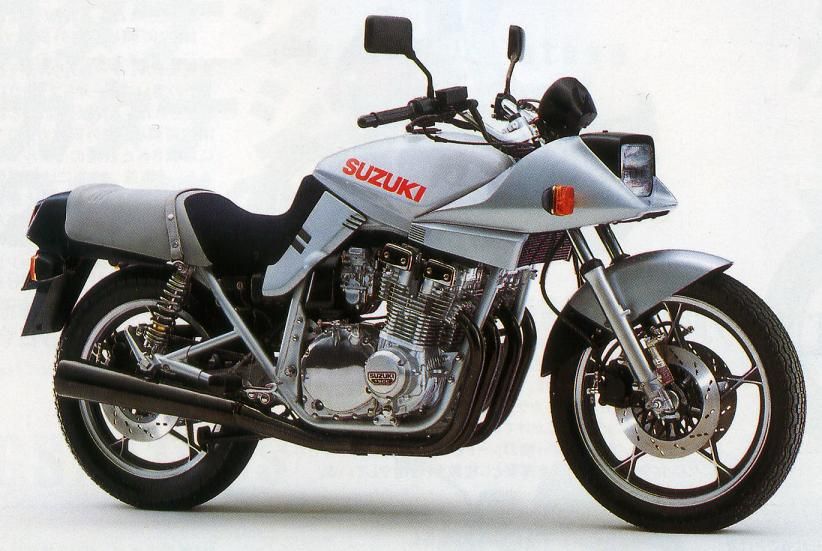
Following in the 1100’s tyre tracks, Suzuki launched the GSX750S Katana in 1981 and it had no windscreen. The model with the windscreen was the 750SS. The 747cc, air-cooled, DOHC, inline-Four produced 68 bhp.
1981 also saw the superbike racing homologated 1000S, since superbike racing capped the engine capacity at 1000cc. it had Mikuni smooth-bore carburettors among other racing accoutrements. This was the rarest Katana and collectors will pay a ransom for one!
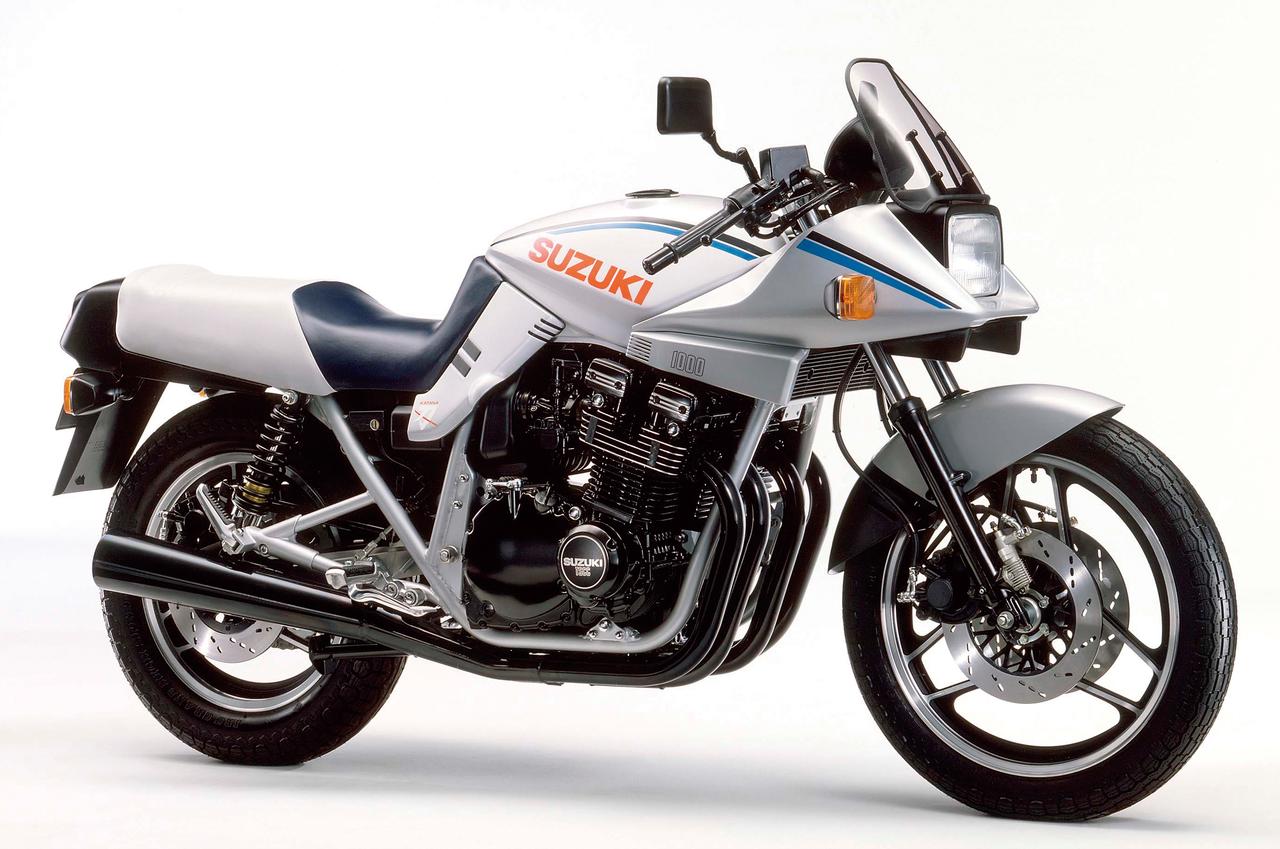
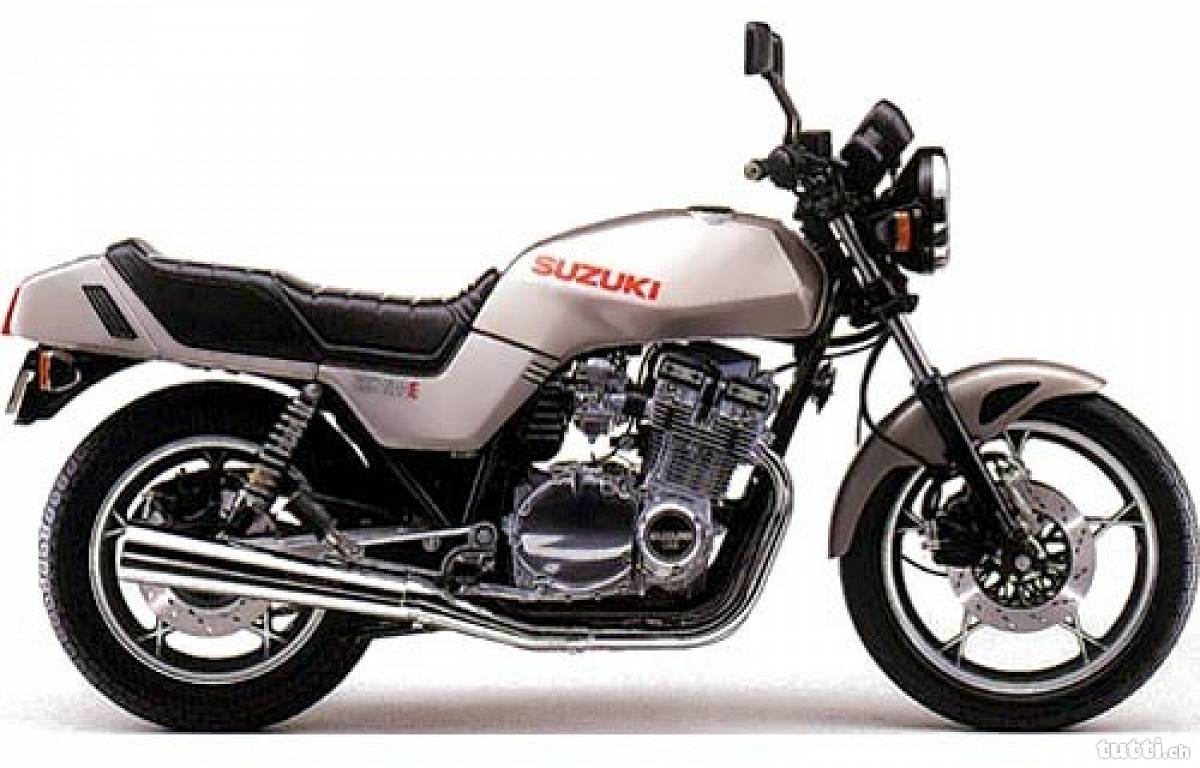
1982 saw the Katana’s futuristic looks being modified to feature a round headlamp and tail unit from the previous year’s GSX1100E for the American market. Buyers there were obviously slow in adapting to change.
Not many changes were afoot for the Katanas in 1983, but it was 1984 when the 750 was forever known as the legend.
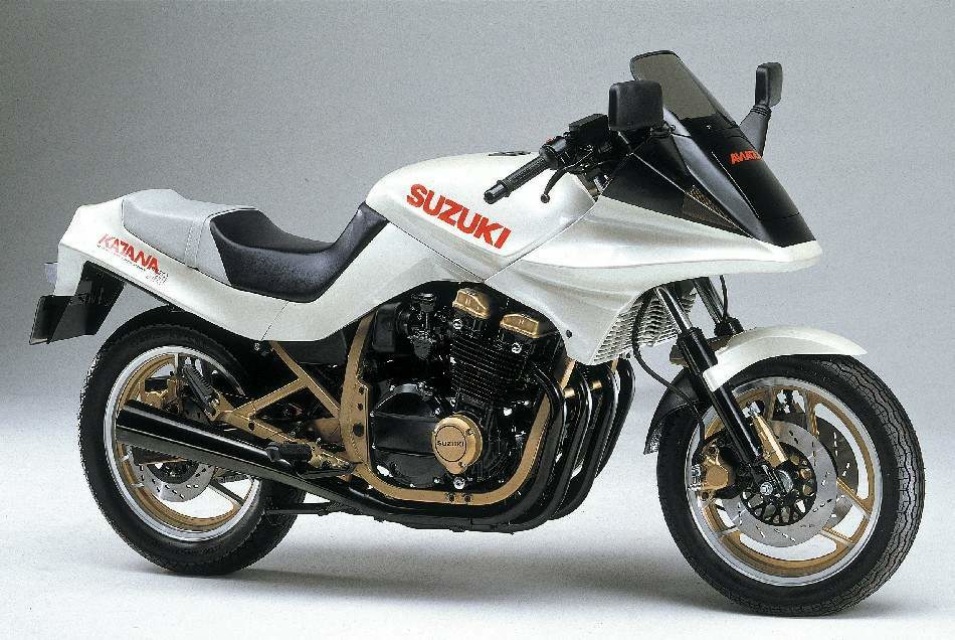
For that year, the GSX750SE Katana was a completely new model. The 16-valve, oil-cooled, inline-Four was taken from the GSX750R/ES/EF and made 90 bhp. It was also given the Positive Damping Forks up front and Suzuki Full Floater rear suspension which did away with the dual shocks. The frame, parts of the wheels and engine were painted in gold.
The most well-known feature was of course the pop-up headlight.
The Suzuki GSX750S continued into its last year of production in 1985 for the worldwide market and 1986 for the domestic market, making these models somewhat rare. Many collectors would love to have one in their collection.
It was sadly the same on the GSX1100S Katana front as it faded in obscurity as Suzuki had launched the GSX-R750F sportbike in 1985. Affectionately known as the “Slabside” or “Slabby,” the first Gixxer heralded the new age of race replica sportbikes and Suzuki went all out to capitalize on it.
Perhaps realizing their mistake, Suzuki in America tried to revive the Katana name in 1988, by slapping the name and symbol on a host of sport-touring and touring models, but it was not to be the same.
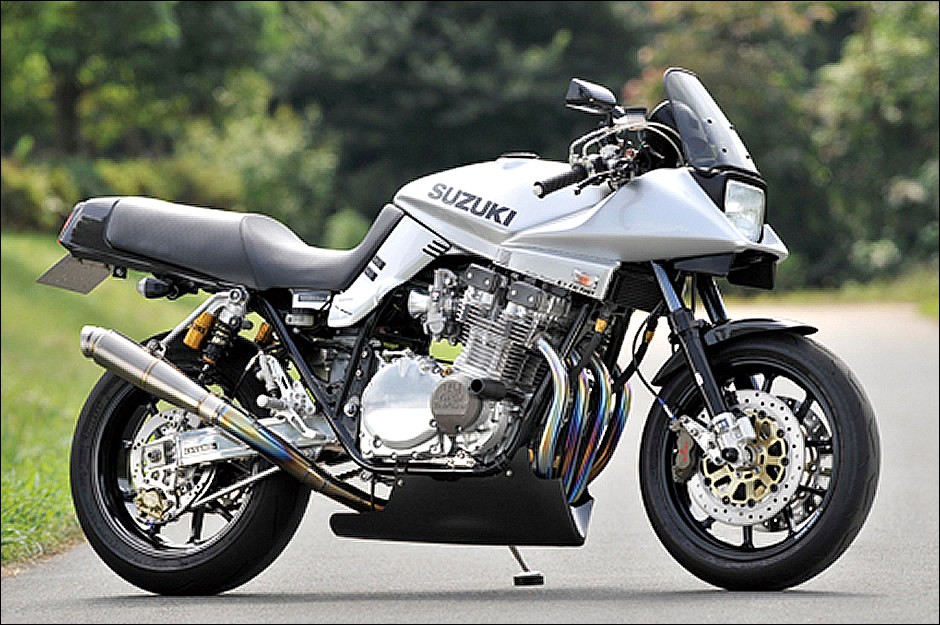
It’s a great shame to lose the Katana as it is still beautiful even after 27 years. It was truly unusual for its time and it still is somewhat today (that’s why there are many customized Katanas around today).
Please click here for Part 1 (Suzuki RE5), here for Part 2 (Honda CBX1000), and here for Part 3 (Yamaha GTS1000).