-
Here are 10 countries ranked by the highest proportion of motorcycle-related deaths.
-
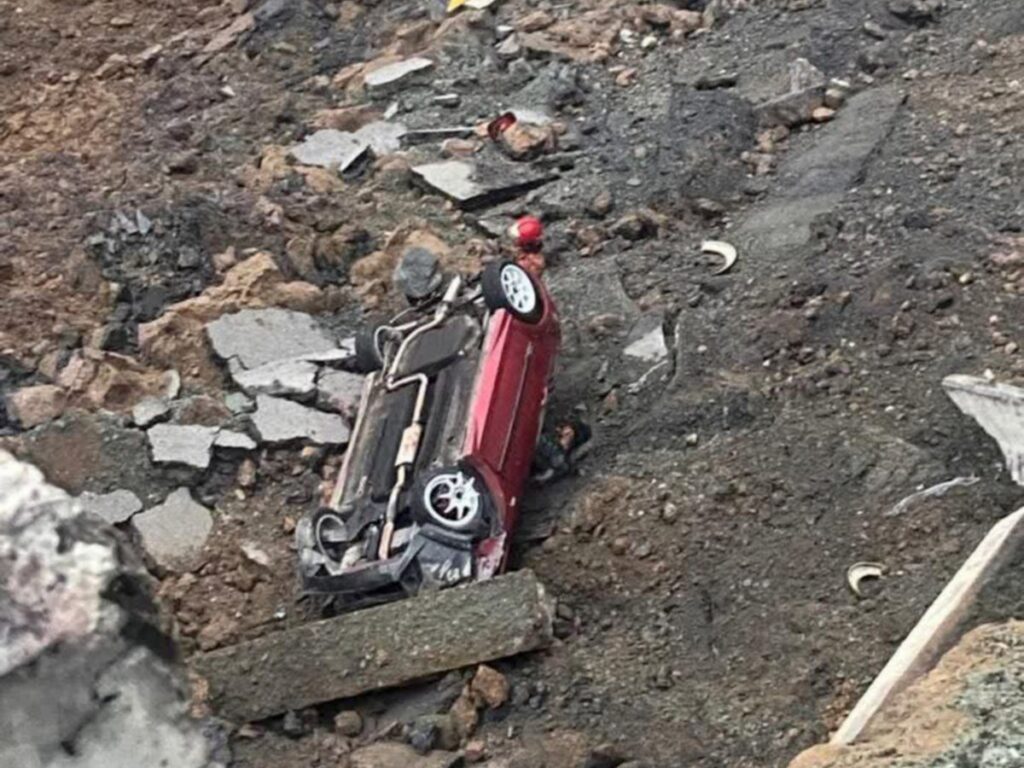
The number of fatalities is staggering, running into the millions in total.
-
Most countries here don’t regulate helmet standards and don’t require motorcyclists to wear helmets.
Here’s something sobering. Motorcycle-related deaths in traffic accidents still account for the highest proportion in most – if not all – countries around the world.
But there are a number of countries in which the proportion of motorcycle-related deaths are higher. Included in this list are a number of countries we often ride to and in.
10. Paraguay – 52.2%
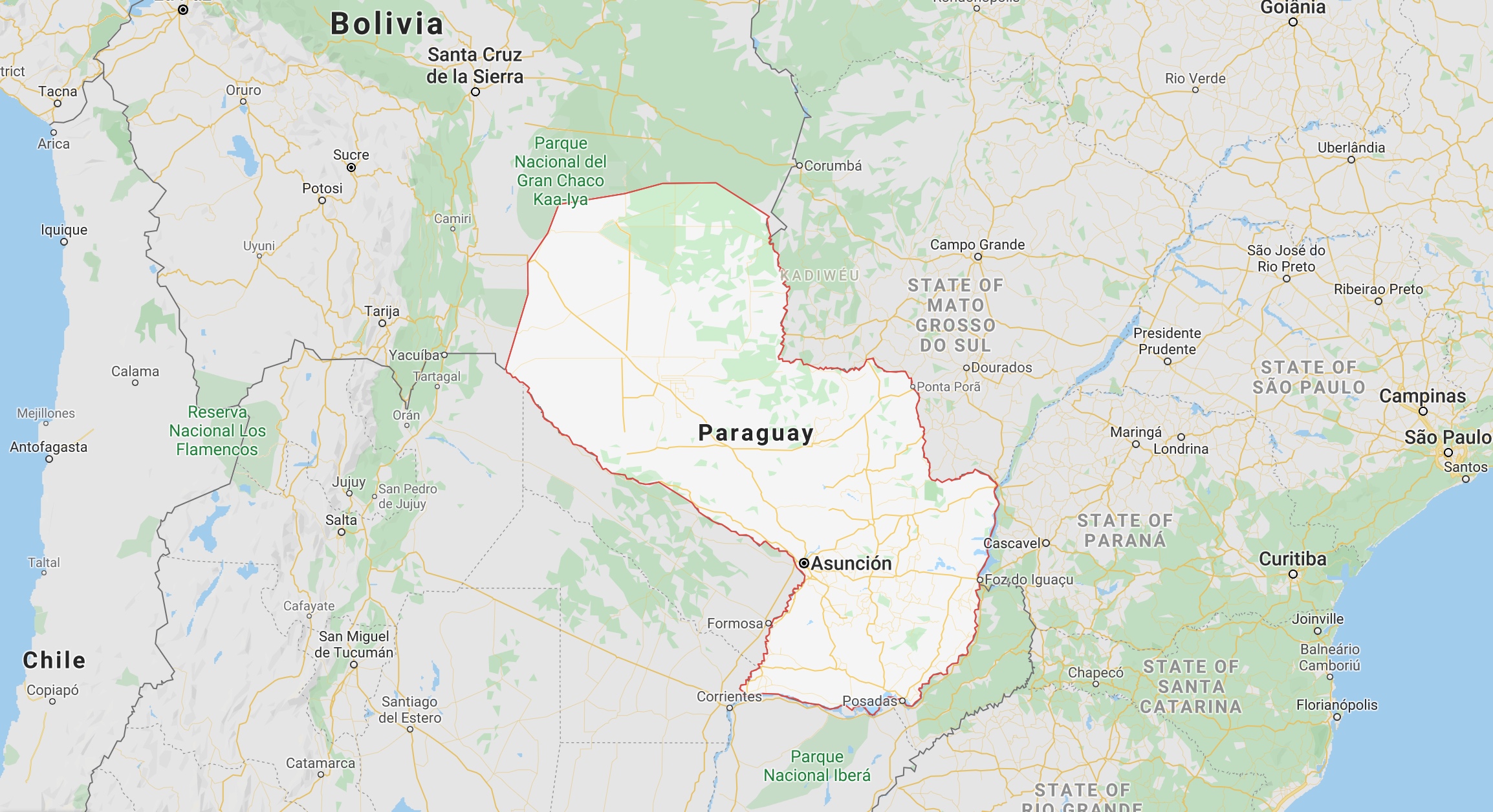
This landlocked South American country has 1.8 million registered vehicles, of nearly 560,000 are motorcycles. Although the proportion of motorcycles are only 30 percent, they contribute to 52.2% of total road fatalities. Ironically, the country practices strict enforcement of their highway code and motorcyclists are required to wear helmets.
9. Colombia – 52.5%
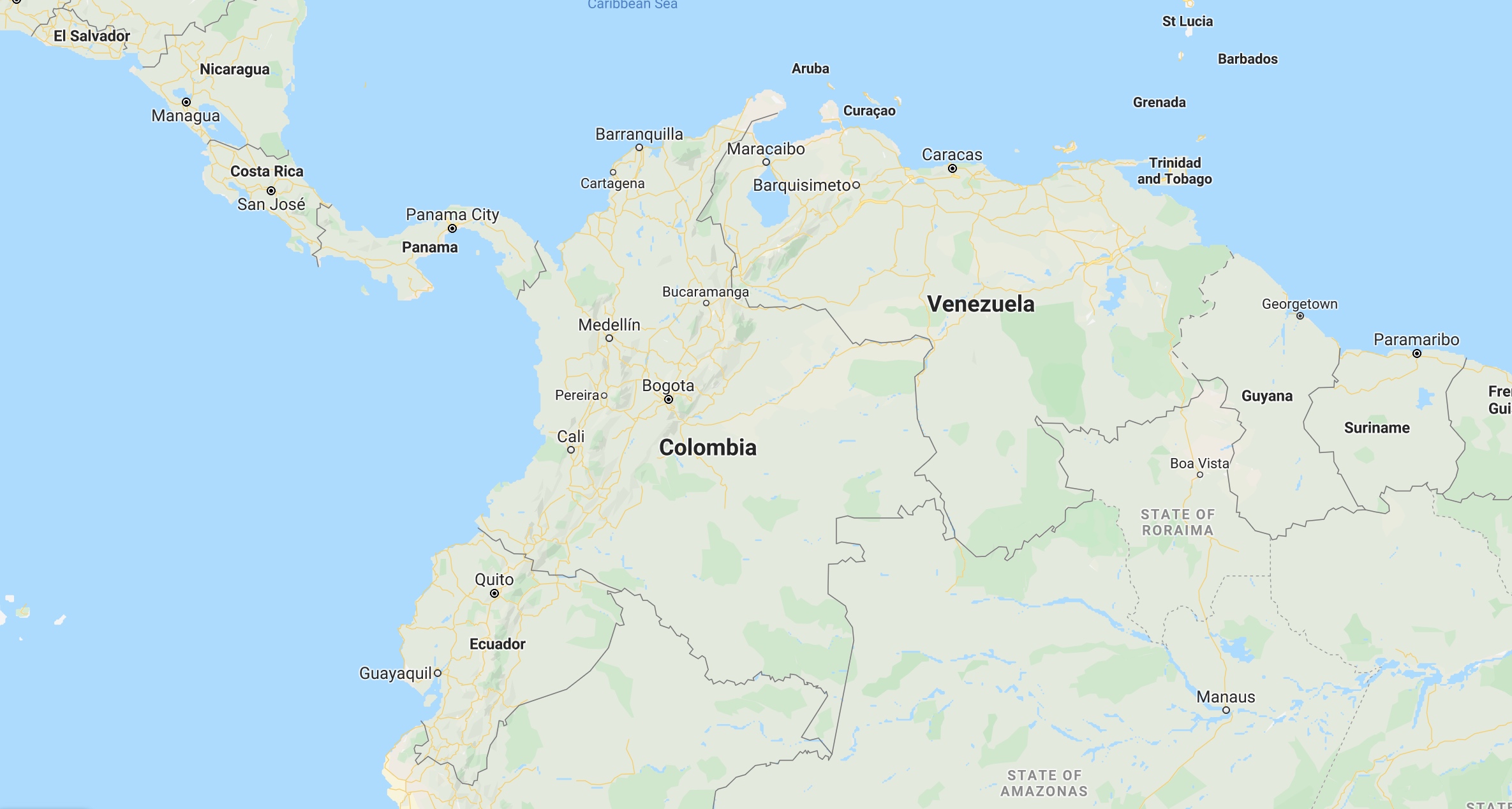
There are more motorcycles than cars in Colombia, to the tune of 55%. While helmet law isn’t enforced, 96% of riders and 80% of their passengers wear helmets. Still, the death rate is a high 52.5% percent.
8. Republic of Benin 56.5%
Benin is located in west Africa. Here, there are no regulations for helmet standards, nor are motorcyclists required to wear helmets. There are 195,000 motorcycles compared to 470,000 cars (41%).
7. Malaysia – 60%
According to the 2016 WHO report, Malaysia has 27,613,120 registered vehicles. 46% of those are motorcycle, totaling 12,677,041. There are helmet laws and the highway code is rather extensive. Helmet quality regulations are also tight. Yet we rank high as one among the countries with the highest number of motorcycle-related deaths in the world. We’ll leave out the why. For now.
6. Myanmar – 64.8%
There are 5.4 million motorcycles among 6.4 million registered vehicles in this country. Like some of the countries in this list, there is no regulation on helmet quality despite the law requiring motorcycles to wear helmets.
5. Dominican Republic – 67%
Motorcycles account for nearly 54% (2.1 million) of the total vehicles in this country. Helmet use isn’t mandatory, hence only some 27% of riders and 2% of passengers wear helmets. The Dominican Republic was ranked with the highest road accident fatality rate in the world in 2013.
4. Republic of Togo – 71.6%
The Republic of Togo is the neighbor to the Republic of Benin. It has only 45,341 registered vehicles. The country doesn’t make helmet use mandatory and it reflects on the large number of fatalities.
3. Cambodia – 73.5%
We’re into the top three. Cambodia has a total of 2,714,913 registered motorcycles. Helmet usage isn’t mandatory here. A survey held that 70% of riders wear helmets during the day but that percentage drops to only 43% at night. Additionally, 30% of the passengers put on helmets during the day but it drops to only 13% at night.
2. Indonesia – 73.6%
Indonesia is currently the biggest motorcycle market in the world. More than half of the country’s 250 million population own a vehicle, and more than half of that are motorcycles. Only 71% of riders wear helmets.
1. Thailand – 74.4%

Thailand holds the unfortunate record as having the most dangerous roads in South East Asia, Asia and additionally the most dangerous for motorcyclists. The government has encouraged motorcyclists to wear helmets, besides the passenger. There seems to be no regulations on helmet quality and standards. The percentage is staggering – almost 3 out of every four deaths were motorcycle-related.
India – 98,700 motorcycle-related fatalities
The country with the highest number of motorcycle-related deaths is India. The WHO estimates that there were 299,091 total traffic-related deaths in subcontinent, 33% of those attributed to motorcycles. While the percentage is low, it is the highest in terms of pure numbers, totaling 98,700 fatalities. The total death rate is so high that it tops the African, Americas, Eastern Mediterranean and European regions. China was second with 256,180 total deaths.